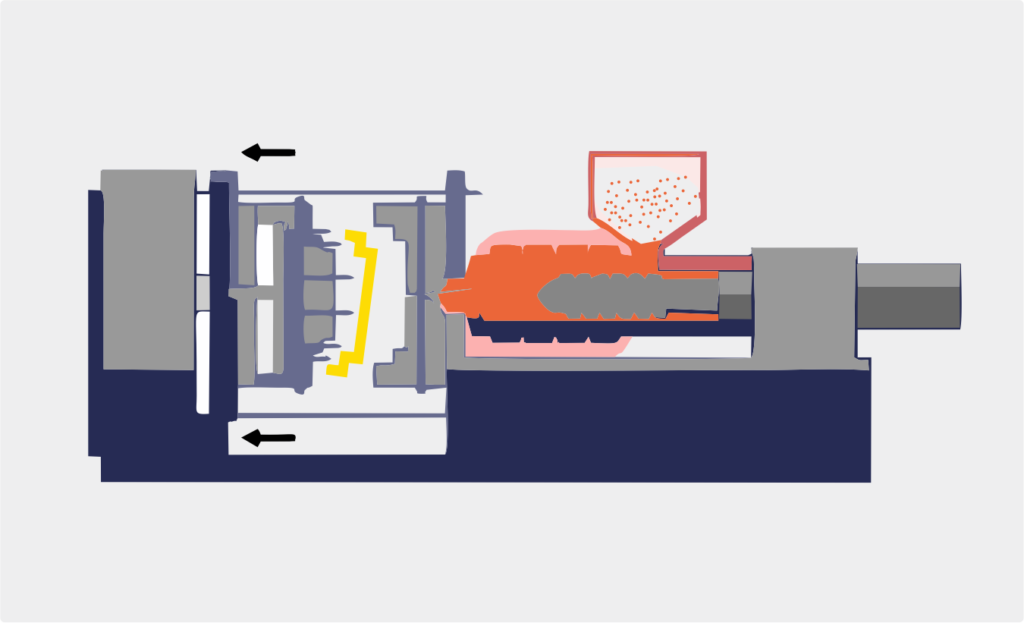
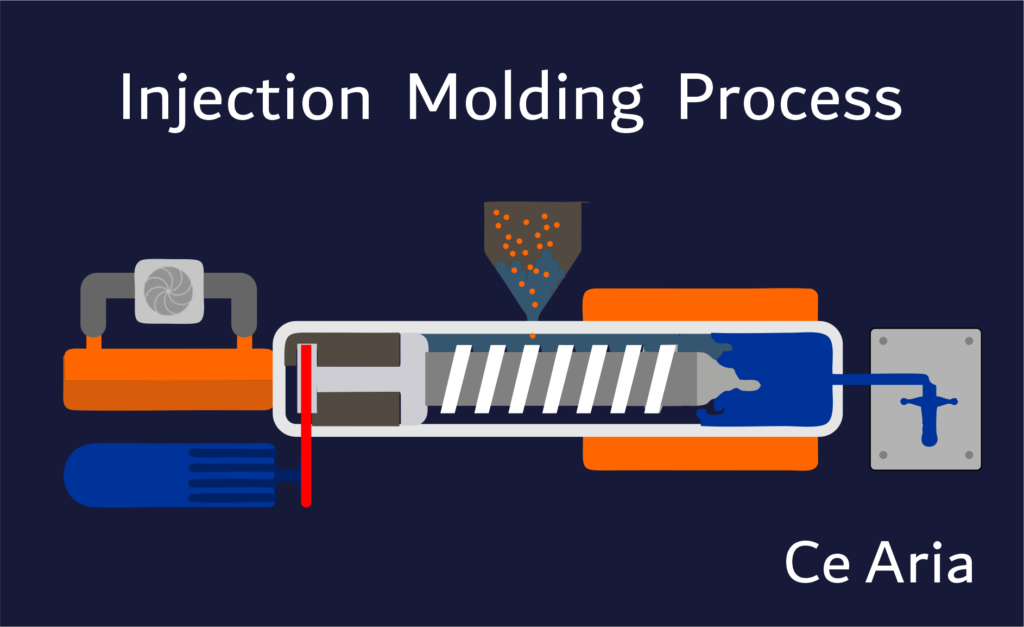
Plastic injection molding is to point to fall in a certain temperature, through screw agitate the plastic material that melts completely, shoot into the mold cavity with high pressure, after classics cooling solidifies, get the method that shape article. The process began in the 1920s, and has nearly a hundred years of development history, and it is currently used very widely, a very mature industrial manufacturing technology.
In the plastic manufacturing industry, 3D printing and injection molding are often pitted against each other, and there are many claims that 3D printing is the end of injection molding. For manufacturers, the competitiveness of the two is also one of their most concerned topics. So what’s the difference between 3D printing and injection molding?
Production models
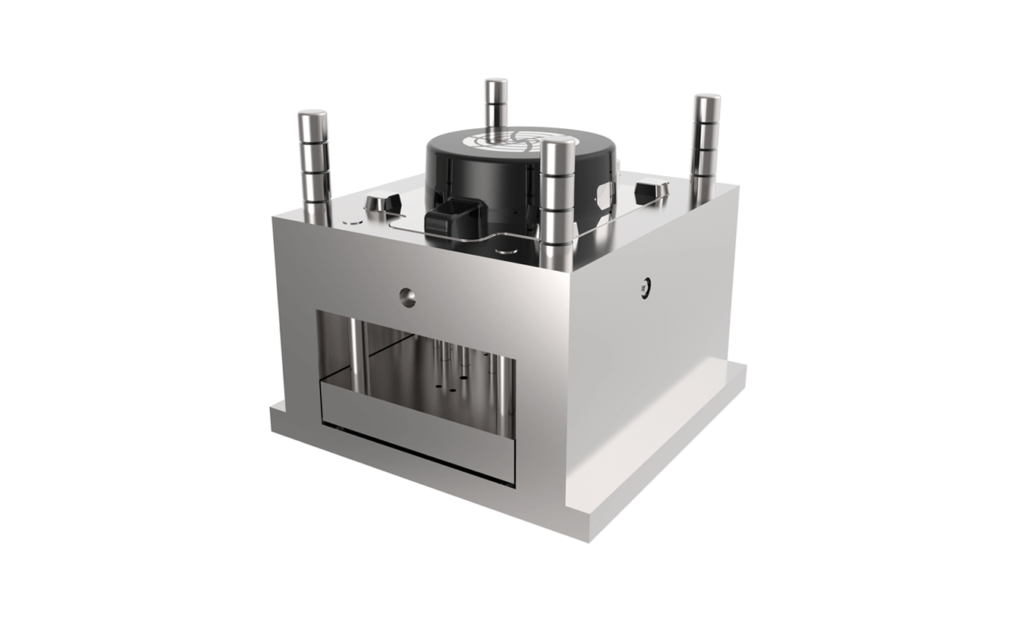
In the injection molding process, you can low-cost, large-scale production of standardized products as long as there is injection mold. Therefore, injection molding is still the best choice for the traditional mass, large-scale manufacturing.
And 3D printers do not need the traditional tooling, fixture, machine tools, or any mould, and they can; the computer directly to any shape of automatic, rapid, direct, and more accurately in the computer 3D design into real models, thanks to the 3D printer is considerably different from the traditional characteristics of the injection molding process, the more complex than solid objects, the faster the processing speed, The more it saves the cost of raw materials, the better it is at the manufacture of personalized and diversified products.
Manufacturing costs
Due to the wide availability of raw materials for injection molding, its large-scale and rapid standardized production characteristics are also conducive to reducing the cost of individual products. Therefore, in terms of manufacturing costs, injection molding is much lower than that of 3D printing technology.
However, for industrial manufacturing, the real cost-saving aspect of 3D printing is modifying the prototype, which only needs to modify the CAD model without any manufacturing costs.
In injection molding, if the prototype is a steel mold, the modification cost is relatively low, but the cost is much higher if the aluminum alloy mold tool is used. This is also why many enterprises or individuals engaged in mold design will choose the 3D printer for mold design and printing.
Application fields

At present, the injection molding process can achieve the mass production of a uniform shape of the item, so it is very suitable for mass standardized product manufacturing.
3D printing can print raw materials into mock-ups or even directly manufacture parts or molds by inputting 3D images through a control terminal, thus effectively shortening the product development cycle. 3D printing has been widely used in makers, architectural design, mold model design,, and other fields.
Adhesive injection metal 3D printing versus injection molding
Metal injection molding (MIM) is a powerful manufacturing process for the mass production of metal parts. But binder jet metal 3D printing offers a compelling alternative with its unique advantages.
The 3D printing of adhesive injection metal uses an array nozzle to slice the CAD model into a series of two-dimensional data. According to the 2d graphics obtained by slicing, the selective injection of binder in the metal powder bed is used to solidify and form, and the whole billet parts are made layer by layer. Then the blank parts go through pre-sintering to get a certain strength, and powder cleaning. Finally, the binder is removed by high-temperature sintering, and the fusion between powder particles is achieved so as to obtain high density and high strength parts. There are similarities and differences between the two technologies.
Similarities and differences between binder injection metal 3D printing and injection molding
First of all, 3D printing has fewer design constraints, and the feature of manufacturing parts layer by layer enables this technology to have better design freedom. In principle, it can realize the printing of parts with various complex shapes. It also means that several parts can be integrated — several connectors can be replaced by a single part but perform the same function — reducing the number of parts and shortening assembly times. MIM’s design allows for smudging of parts, limiting some shapes and making it impossible to create complex structures like 3D printing. However, due to the influence of gravity, friction, and shrinkage, the sintering process of binder injection metal 3D printing is not good at processing large-area thin-walled parts without a support structure, and is not good at producing fine-twig tree-like parts.
Secondly, the molding process is different. The 3D printing of adhesive injection metal is made by selective injection of adhesive by array nozzle, while the MIM is made by mold injection molding. But the post-treatment process is the same, and both need high-temperature sintering. After sintering, the density of 3D printed parts can reach more than 98%, which is similar to the MIM process. But because MIM requires a special degreasing process, it is impossible to make very thick parts.
Third, binder injection metal 3D printing has fewer manufacturing steps than MIM. MIM requires mold opening, whereas binder jet metal 3D printing can print parts directly. Because for small batch processing speed is obviously better than MIM process. Also, it is not easy to adjust once the MIM mold is finished. So metal 3D printing can go through multiple iterations without increasing the cost.
How to choose between binder injection metal 3D printing and MIM?
In most cases, the trade-off depends on yield. The former is a good choice for prototyping and small batches, such as tens of thousands of units. However, MIM is more cost-effective for mass production, such as hundreds of thousands of units can choose the MIM process.
Besides yield being the determining factor, there are other reasons.
Due to degreasing limitations, MIM cannot be made with too many thick parts. Generally, the mass of MIM parts is below 500g, so for large-size parts, the 3D printing process is preferred.
In addition, complex designs tend to opt for 3D printing because the geometry of MIM parts is limited by demoulding.
There are also differences in surface quality between the two processes. MIM has a slightly higher surface finish, with a roughness of about 1-2 μm, while the surface roughness of 3D printed parts with adhesive spray metal is above 3μ. CNC is needed for the post-processing process for those with higher assembly accuracy requirements, which can be either injection molding or 3D printing.
No matter what kind of process form of 3D printing, it is a beneficial supplement to the traditional manufacturing process. For some small batch and complex products, the cost of mold opening or other traditional processes is relatively high. At this time, 3D printing may have more obvious price advantages and manufacturing efficiency. Therefore, in the future, as specific industries deepen their understanding of 3D printing technology, this technology will become a choice in the industry chain. 3D printing is just a process.